Publish entities to Lattice
This page covers how to create and update different types of known objects, known as entities in Lattice,
with the Lattice SDK. For reference, see PublishEntity
(gRPC | HTTP).
Before you begin
- To publish entities, set up your Lattice environment.
- Learn about required components and various entity shapes in Lattice.
Publish an asset
Use the PublishEntity (gRPC | HTTP)
API method to publish a drone asset:
- Add the required components to the entity object.
- Set the asset
ontology.templatetoTEMPLATE_ASSET. - Set the
locationfield. - Set the
milViewfield.
Drone
For example, to create an entity for a drone, you would define ontology, milView, and location.
Optionally, you can define a taskCatalog to describe the tasks the asset can perform. For more information about
tasking an asset, see Tasking.
- Ontology
- MilView
- Location
"ontology": {
// Set the required template.
"template": "TEMPLATE_ASSET",
// Optionally, set platform_type to UAV.
"platform_type": "UAV"
}
"milView": {
// Set the disposition to friendly.
// Assets are generally under the control of friendly forces.
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_FRIENDLY",
// Set the environment field to specify the terrain in which
// your asset is operating
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_AIR"
}
"location": {
// Set the position of the asset.
"position": {
// Set the asset's lattitude, expressed in degrees.
"latitudeDegrees": 50.91402185768586,
// Set the asset's longitude, expressed in degrees.
"longitudeDegrees": 0.79203612077257,
// Set the asset's Height Above Ellipsoid (HAE), expressed in meters.
"altitudeHaeMeters": 2994,
// Set the asset's Above Ground Level (AGL) altitude, expressed in meters.
"altitudeAglMeters": 2972.8
}
}
Together with the entity model's required components, you get the following entity object:
{
"entityId": "UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID",
"description": "Asset",
"isLive": true,
"createdTime": "2024-12-07T00:09:42.816877Z",
"expiryTime": "2024-12-17T00:09:42.816878Z",
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 50.91402185768586,
"longitudeDegrees": 0.79203612077257,
"altitudeHaeMeters": 2994,
"altitudeAglMeters": 2972.8
}
},
"aliases": {
"name": "UAV"
},
"milView": {
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_FRIENDLY",
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_AIR"
},
"ontology": {
"template": "TEMPLATE_ASSET",
"platform_type": "UAV"
},
"taskCatalog": {
"taskDefinitions": [
{
"taskSpecificationUrl": "type.googleapis.com/anduril.tasks.v2.VisualId",
}
],
},
"health": {
"healthStatus": "HEALTH_STATUS_HEALTHY"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your integration",
"dataType": "your_data_type",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-07T00:19:47.706196Z"
}
}
The following publishes a drone asset that moves in a circle around Southern California, receiving an update every 10 milliseconds:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, Aliases, \
Entity, MilView, Location, Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance, Health, HealthStatus
from anduril.ontology.v1 import Disposition
# Import TaskCatalog and TaskDefinition to define tasks
# that your asset can perform.
from anduril.tasks.v2 import TaskCatalog, TaskDefinition
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import math
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token" \
"have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set" \
"as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
count = 0
radius_degrees = .1
t = math.radians(count)
creation_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
id = str(uuid4())
print(f"Publishing simulated asset: {id}")
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
count += .1
entity = Entity(
entity_id = id,
created_time=creation_time,
aliases=Aliases(name="Simulated Drone"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=10),
mil_view=MilView(disposition=Disposition.FRIENDLY),
location=Location(
position=Position(
# Move the entity in a circle.
latitude_degrees=33.69447852698943 + (radius_degrees * math.cos(t)),
longitude_degrees=-117.9173785693163 + (radius_degrees * math.sin(t)))),
ontology=Ontology(
template=Template.ASSET,
platform_type="UAV"
),
task_catalog=TaskCatalog(
task_definitions=[
TaskDefinition(
task_specification_url="type.googleapis.com/anduril.tasks.v2.VisualId"
)
]
),
health=Health(
health_status=HealthStatus.HEALTHY
),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_test_integration",
data_type="your_data_type",
source_update_time=time_now),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(.01)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Publish a track
Use the PublishEntity (gRPC | HTTP)
API method to publish a track:
- Add the required components to the entity object.
- Set the asset
ontology.templateto one of the following options:TEMPLATE_TRACK|TEMPLATE_SENSOR_POINT_OF_INTEREST|TEMPLATE_SIGNAL_OF_INTEREST. For more information, see Entity shapes. - Set the
locationfield. - Set the
milViewfield. In most cases, the asset assesses the disposition of the track and updates this component according to the latest state of the world in Lattice. A trackmilViewmight update from suspicious to hostile as more information is known about the track.
Generic track
To create a generic track, for example to represent a person or animal, set ontology.template to TEMPLATE_TRACK, then define
the location, milView, and components:
- Ontology
- MilView
- Location
"ontology": {
// Set the required template.
"template": "TEMPLATE_TRACK",
// Optionally, set platform_type to PERSON.
"platform_type": "PERSON"
}
"milView": {
// Set the disposition.
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_ASSUMED_FRIENDLY",
// Set the environment field to specify the terrain in which
// the person is observed.
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SURFACE"
}
"location": {
// Set the position of the asset.
"position": {
// Set the asset's lattitude, expressed in degrees.
"latitudeDegrees": 50.0,
// Set the asset's longitude, expressed in degrees.
"longitudeDegrees": 0.70
}
}
Together with the entity model's required components, you get the following entity object:
{
"entityId": "fb6557ae-19e7-44a0-bbe3-6e1bba16094c",
"description": "Person track",
"isLive": true,
"expiryTime": "2025-04-22T18:40:35.310Z",
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 50.91402185768586,
"longitudeDegrees": -0.79203612077257
}
},
"aliases": {
"name": "Person"
},
"milView": {
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_ASSUMED_FRIENDLY",
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SURFACE"
},
"ontology": {
"platformType": "PERSON",
"template": "TEMPLATE_TRACK"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your_integration_name",
"dataType": "your_data_type",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-22T18:30:35.310Z",
}
}
Use the following to publish a track:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, Aliases, \
Entity, MilView, Location, Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance
from anduril.ontology.v1 import Disposition, Environment
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
creation_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
id = str(uuid4())
print(f"Publishing entity {id}")
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
entity = Entity(
entity_id = id,
created_time=creation_time,
aliases=Aliases(name="Person"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=10),
mil_view=MilView(
disposition=Disposition.ASSUMED_FRIENDLY,
environment=Environment.SURFACE),
location=Location(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=50.91402185768586,
longitude_degrees=-0.79203612077257
)),
ontology=Ontology(
# Define template as the generic TRACK trype.
template=Template.TRACK,
# Set platform_type to PERSON to create
# the correct visual icon in Lattice.
platform_type="PERSON"),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_integration_name",
data_type="your_data_type",
source_update_time=time_now),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Sensor point of interest (SPI)
To create a sensor point of interest such as a radar, set ontology.template to TEMPLATE_SENSOR_POINT_OF_INTEREST,
then define the milView, and location components. Optionally, you can add sensors
to describe its type and other sensor-related information:
- Ontology
- MilView
- Location
- Sensors
"ontology": {
// Set the required template.
"template": "TEMPLATE_SENSOR_POINT_OF_INTEREST",
// Optionally, set platform_type to RADAR.
"platform_type": "RADAR"
}
"milView": {
// Set the disposition.
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_SUSPICIOUS",
// Set the environment field to specify the terrain in which
// the track is observed.
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SURFACE"
}
"location": {
// Set the position of the asset.
"position": {
// Set the asset's lattitude, expressed in degrees.
"latitudeDegrees": 50.0,
// Set the asset's longitude, expressed in degrees.
"longitudeDegrees": 0.70
}
}
"sensors": {
"sensors": [
{
"operationalState": "OPERATIONAL_STATE_OPERATIONAL",
"sensorType": "SENSOR_TYPE_RADAR"
}
]
}
Together with the entity model's required components, you get the following entity object:
{
"entityId": "UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID",
"description": "Radar",
"isLive": true,
"createdTime": "2025-12-07T00:09:42.816877Z",
"expiryTime": "2025-12-17T00:09:42.816878Z"
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 52.0,
"longitudeDegrees": 0.70
}
},
"aliases": {
"name": "Radar"
},
"milView": {
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_SUSPICIOUS",
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SURFACE"
},
"ontology": {
"template": "TEMPLATE_SENSOR_POINT_OF_INTEREST",
"platform_type": "RADAR"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your_integration",
"dataType": "your_data_type",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-07T00:19:47.706196Z"
}
}
Use the following to publish a sensor point of interest:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, \
Aliases,Entity, MilView, Location, Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance, \
Sensors, Sensor, SensorType, OperationalState
from anduril.ontology.v1 import Disposition, Environment
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
creation_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
id = str(uuid4())
print(f"Publishing entity {id}")
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
entity = Entity(
entity_id = id,
created_time=creation_time,
aliases=Aliases(name="Radar 1"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=10),
mil_view=MilView(
disposition=Disposition.ASSUMED_FRIENDLY,
environment=Environment.SURFACE),
location=Location(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=50.91402185768586,
longitude_degrees=-0.79203612077257
)),
ontology=Ontology(
template=Template.TRACK,
platform_type="RADAR"),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_integration_name",
data_type="adsb",
source_update_time=time_now),
sensors=Sensors(
sensors=[
Sensor(
sensor_type=SensorType.RADAR,
operational_state=OperationalState.OPERATIONAL
)
]
),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Signal of interest (SOI)
To create a signal of interest, such as a satellite being tracked by one of your assets, you would define ontology, milView, and
signal. Optionally, you define a location if your signal.fixed
is set, meaning that the detected signal is at a fixed location.
- Ontology
- MilView
- Signal
- Location
"ontology": {
// Set the required template.
"template": "TEMPLATE_SIGNAL_OF_INTEREST",
// Optionally, set platform_type to RADAR.
"platform_type": "RADAR"
}
"milView": {
// Set the disposition.
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_SUSPICIOUS",
// Set the environment field to specify the terrain in which
// the track is observed.
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SURFACE"
}
// Add signal details.
"signal": {
// Indicates that the signal is detected at a fixed location.
// Requires setting the location component.
"fixed": {}
}
// If signal.fixed is set, add location.
"location": {
// Set the position of the asset.
"position": {
// Set the asset's lattitude, expressed in degrees.
"latitudeDegrees": 50.0,
// Set the asset's longitude, expressed in degrees.
"longitudeDegrees": 0.70
}
}
Together with the entity model's required components, you get the following entity object:
{
"entityId": "UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID",
"description": "",
"isLive": true,
"createdTime": "2025-04-21T20:42:42.741Z",
"expiryTime": "2025-04-21T21:17:38.156Z",
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 50.91401185768586,
"longitudeDegrees": -0.79203612077257,
"altitudeHaeMeters": 300000
}
},
"aliases": {
"name": "Signal 1"
},
"milView": {
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_SUSPICIOUS",
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_SPACE",
},
"ontology": {
"template": "TEMPLATE_SIGNAL_OF_INTEREST",
"platformType": "SATELLITE"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your_integration_name",
"dataType": "adsb",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-21T20:47:38.156Z",
},
"signal": {
"fixed": {}
}
}
Use the following code to create a satellite track detected in the South of England:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, Aliases, \
Entity, MilView, Location, Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance, Signal, Fixed
from anduril.ontology.v1 import Disposition, Environment
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
creation_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
id = str(uuid4())
print(f"Publishing entity {id}")
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
entity = Entity(
entity_id = id,
created_time=creation_time,
aliases=Aliases(name="Signal 1"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=30),
mil_view=MilView(
disposition=Disposition.SUSPICIOUS,
environment=Environment.SPACE),
location=Location(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=50.91401185768586,
longitude_degrees=-0.79203612077257,
altitude_hae_meters=300000
)),
ontology=Ontology(
template=Template.SIGNAL_OF_INTEREST,
platform_type="SATELLITE"),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_integration_name",
data_type="adsb",
source_update_time=time_now),
signal=Signal(
fixed=Fixed()
),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Publish a geo-entity
Use the PublishEntity (gRPC | HTTP)
API method to publish a geo-entity:
- Add the required components to the entity object.
- Set
ontology.templatetoTEMPLATE_GEO. - Set the
geo_shapefield. - Set the
geo_detailsfield. - Set the
locationfield if publishing an ellipse.
Polygon
To create a geo-entity in the shape of a generic polygon, you would define ontology, geoShape,
and geoDetails.
For polygons, geoShape is set to polygon.
You define rings for the polygon. Each ring must have at least four defined points, represented by a position
component.
The last point must be the same as the first point you define for the ring component.
The following JSON example demonstrates a three-sided polygon. Each position defined in the ring has a minimum altitude
defined by the altitude_agl_meters field. The first, and the last positions, define a heightM component
representing additional height above the minimum altitude set by altitude_agl_meters:
- Ontology
- GeoDetails
- GeoShape
"ontology": {
// Set the required template.
"template": "TEMPLATE_GEO"
}
"geoDetails": {
// Set the type of the geo-entity to GEO_TYPE_GENERAL.
"type": "GEO_TYPE_GENERAL"
}
"geoShape": {
"polygon": {
"rings": [
{
"positions": [
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01611140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 1.5746513124955297,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
},
"heightM": 20.00
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01924140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 2.882469645828863,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
}
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 48.4172380712981,
"longitudeDegrees": 2.9189863124955298,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
}
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01611140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 1.5746513124955297,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
},
"heightM": 20.00
}
]
}
],
}
}
Together with the entity model's required components, you get the following entity object:
{
"entityId": "UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID",
"isLive": true,
"expiryTime": "2025-04-21T21:09:29.454Z",
"aliases": {
"name": "Polygon 1"
},
"ontology": {
"template": "TEMPLATE_GEO"
},
"geoShape": {
"polygon": {
"rings": [
{
"positions": [
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01611140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 1.5746513124955297,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
},
"heightM": 20.00
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01924140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 2.882469645828863,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
}
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 48.4172380712981,
"longitudeDegrees": 2.9189863124955298,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
}
},
{
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 49.01611140463143,
"longitudeDegrees": 1.5746513124955297,
"altitude_agl_meters": 50.00
},
"heightM": 20.00
}
]
}
],
}
},
"geoDetails": {
"type": "GEO_TYPE_GENERAL"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your_integration_name",
"dataType": "your_data_type",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-21T20:59:29.454Z",
}
}
Use the following code to create a polygon:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, Aliases, \
Entity,Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance, GeoShape, GeoPolygon, GeoPolygonPosition, \
GeoDetails, GeoType, GeoPolygon, LinearRing
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
creation_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
id = str(uuid4())
print(f"Publishing entity {id}")
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
entity = Entity(
entity_id = id,
created_time=creation_time,
aliases=Aliases(name="Polygon 1"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=10),
geo_shape=GeoShape(
polygon=GeoPolygon(
rings=[
LinearRing(
positions=[
GeoPolygonPosition(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=49.01611140463143,
longitude_degrees=1.5746513124955297,
altitude_agl_meters=50.00
),
height_m=1.0
),
GeoPolygonPosition(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=49.01924140463143,
longitude_degrees=2.882469645828863
)
),
GeoPolygonPosition(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=48.4172380712981,
longitude_degrees=2.9189863124955298
)
),
GeoPolygonPosition(
position=Position(
latitude_degrees=49.01611140463143,
longitude_degrees=1.5746513124955297,
altitude_agl_meters=50.00
),
height_m=1.0
)
]
),
]
)
),
geo_details=GeoDetails(
type=GeoType.GENERAL
),
ontology=Ontology(
template=Template.GEO),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_integration_name",
data_type="your_data_type",
source_update_time=time_now),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Assign entity icons
For iconography within Lattice, add a platform_type value to the ontology component of the entity data model. See the list of available values:
List of platform_type values supported in Lattice:
- Air Vehicle
- Animal
- Battleship
- Bomber
- Car
- Fighter
- Missile
- Mortar
- Person
- Radar
- Satellite
- Surface Vessel
- Submarine
- Tank
- UAV
- Vehicle
See the following example iconography:
Platform Type - Car

Platform Type - Surface Vessel

Specify motion
The
location
component contains kinematic fields, including position, attitude, and velocity,
that represent the motion of entities over time. Third-party integrations are
responsible for providing all available kinematic field data.
Altitude
The data model contains four altitude references, specified in meters:
altitude_hae_meters: The entity's height above the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84) ellipsoid.altitude_agl_meters: The entity's height above the terrain. This is typically measured with a radar altimeter or by using a terrain tile set lookup.altitude_asf_meters: The entity's height above the sea floor.pressure_depth_meters: The depth of the entity from the surface of the water.
The data model does not currently support Mean Sea Level (MSL) references,
such as the Earth Gravitational Model 1996 (EGM-96) and the Earth Gravitational
Model 2008 (EGM-08). If the only altitude reference available to your
integration is MSL, convert it to Height Above Ellipsoid (HAE) and populate the
altitude_hae_meters field. There are many open source libraries available (for
example: Go) that allow for this
conversion.
For example, to indicate to Lattice that a plane is flying at an altitude of 2,994 meters above the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS-84) ellipsoid, you would populate an entity with the following data:
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 42.2,
"longitudeDegrees": -71.1,
"altitudeHaeMeters": 2994.0,
"altitudeAglMeters": 2972.8
},
}
Attitude
The entity's attitude is represented by a quaternion in the attitude_enu
field. This representation is used to translate from the entity's body frame to
its East-North-Up (ENU) frame. If the attitude_enu field isn't populated,
Lattice will use the velocity_enu field to calculate the heading for display
in Lattice UI. If both fields are populated, Lattice will prioritize the value
from attitude_enu.
For example, if your entity has a yaw value of 40 degrees, you would need to
convert to the attitude_enu values with the following:
import math
from typing import List
from anduril.type import Quaternion
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import Entity, Location
def yaw_to_quaternion_enu(yaw_degrees: float) -> List[float]:
# Convert degrees to radians.
yaw_rad = math.radians(90 - yaw_degrees) # Adjust NED yaw by 90 degrees for ENU.
qw = math.cos(yaw_rad * 0.5)
qz = math.sin(yaw_rad * 0.5)
return [qw, 0, 0, qz]
quaternion = yaw_to_quaternion_enu(40)
entity = Entity(
location = Location(
attitude_enu = Quaternion(
w = quaternion[0],
x = quaternion[1],
y = quaternion[2],
z = quaternion[3],
)
)
)
Specify health
Use the health component to define the health status that the entity reports.
This component should only be used for health status that the entity reports back to you. For example, health status should be updated
based on telemetry or health reports over a radio or network connection. You should not add a health component
to tracks whose telemetry or other health reporting data you do not have access to.
When an asset sends an update to Lattice, the health.connection_status
field changes to CONNECTION_STATUS_ONLINE. If there are no updates after one minute, the field value changes to CONNECTION_STATUS_OFFLINE.
For example, in the previous example you published a drone asset with the following health status:
"health": {
"connectionStatus": "CONNECTION_STATUS_ONLINE",
"healthStatus": "HEALTH_STATUS_HEALTHY"
}
Consider a scenario where the asset, due to underlying maintenance issues, needs to update its status to HEALTH_STATUS_WARN to let an operator
know that there might be a problem to address. To do this, the asset must update the health component to the following:
{
"entityId": "UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID",
"description": "Drone",
"isLive": true,
"createdTime": "2025-04-22T05:29:08.333Z",
"expiryTime": "2025-04-22T06:02:35.996Z",
"location": {
"position": {
"latitudeDegrees": 33.79447852698943,
"longitudeDegrees": -117.9173785693163
}
},
"aliases": {
"name": "Drone"
},
"milView": {
"disposition": "DISPOSITION_FRIENDLY",
"environment": "ENVIRONMENT_AIR"
},
"ontology": {
"platformType": "UAV",
"template": "TEMPLATE_ASSET"
},
"provenance": {
"integrationName": "your_test_integration",
"dataType": "your_data_type",
"sourceUpdateTime": "2025-04-22T05:52:35.996Z",
},
"health": {
"connectionStatus": "CONNECTION_STATUS_INVALID",
"healthStatus": "HEALTH_STATUS_WARN",
"components": [
{
"id": "$UNIQUE_ID",
"name": "Drone",
"health": "HEALTH_STATUS_WARN",
"messages": [
{
"status": "HEALTH_STATUS_INVALID",
"message": "Drone $UNIQUE_ENTITY_ID has not been re-calibrated for more than 30 days."
}
]
}
],
"activeAlerts": []
}
}
Use the following code to update the asset's health status to HEALTH_STATUS_WARN:
- Python
app.py
from anduril.entitymanager.v1 import EntityManagerApiStub, PublishEntityRequest, Aliases, \
Entity, MilView, Location, Position, Ontology, Template, Provenance, Health, HealthStatus, \
ComponentHealth, ComponentMessage
from anduril.ontology.v1 import Disposition
from anduril.tasks.v2 import TaskCatalog, TaskDefinition
from grpclib.client import Channel
from uuid import uuid4
from datetime import datetime, timezone, timedelta
import asyncio
import os
import sys
lattice_url = os.getenv('LATTICE_URL')
sandboxes_token = os.getenv('SANDBOXES_TOKEN')
environment_token = os.getenv('ENVIRONMENT_TOKEN')
# Retrieve your environment token and Lattice URL from environment variables.
if not environment_token or not lattice_url:
print("Make sure your Lattice URL and bearer token" \
"have been set as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
# Retrieve the sandboxes token if you are developing on Lattice Sandboxes.
if not sandboxes_token:
print("Make sure your sandboxes token has been set" \
"as system environment variables.")
sys.exit(1)
metadata = {
'authorization': f"Bearer {environment_token}",
'anduril-sandbox-authorization': f"Bearer {sandboxes_token}"
}
async def publish_entity(entity):
channel = Channel(host=lattice_url, port=443, ssl=True)
stub = EntityManagerApiStub(channel)
request = PublishEntityRequest(entity=entity)
response = await stub.publish_entity(request, metadata=metadata)
channel.close()
return response
async def main():
try:
while (True):
time_now = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
count += .1
entity = Entity(
entity_id = "$YOUR_ENTITY_ID",
aliases=Aliases(name="Simulated Drone"),
expiry_time=time_now + timedelta(minutes=10),
mil_view=MilView(disposition=Disposition.FRIENDLY),
location=Location(
position=Position(
# Move the entity in a circle.
latitude_degrees=33.69447852698943,
longitude_degrees=-117.9173785693163
)
),
ontology=Ontology(
template=Template.ASSET,
platform_type="UAV"
),
task_catalog=TaskCatalog(
task_definitions=[
TaskDefinition(
task_specification_url="type.googleapis.com/anduril.tasks.v2.VisualId"
)
]
),
# Define the health of the asset.
health=Health(
# Set the asset's health status to WARN.
health_status=HealthStatus.WARN,
components=[
ComponentHealth(
id="$YOUR_ENTITY_ID",
name="Drone",
health=HealthStatus.WARN,
messages=[
# Add a message to better inform the operator about possible resolutions.
ComponentMessage(
message=f"Drone {id} has not been re-caliberated for more than 30 days."
)
]
)
]
),
provenance=Provenance(
integration_name="your_test_integration",
data_type="your_data_type",
source_update_time=time_now),
is_live=True)
await publish_entity(entity)
await asyncio.sleep(1)
except asyncio.CancelledError:
print(">>>Exiting...")
except Exception as error:
print(f"Exception: {error}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
ADS-B
To indicate that an entity has an ADS-B transponder, there are a few components on the Entity that can be set. Specifically:
Transponder Codes
The Transponder Code mode should be sent depending on if it is a military or civilian aircraft. For civilian aircraft it's common
to have a 24-bit ICAO address to uniquely identify an aircraft. In order to add a badge to Lattice with the ADS-B identifier,
populate the Mode-S.Address field.
Aliases.Name
If there is a flight number associated with the aircraft (e.g. UAL 1393), it's expected to set it as the name of the Entity within aliases.name.
The call sign of the aircraft can also be associated in a structured way as an alternate ID within the aliases.alternate_ids.id field. This should
have an alt ID type of ALT_ID_TYPE_CALLSIGN.
The end result of populating these fields on the Entity are that the Lattice UI renders the specific details in the Entity card:
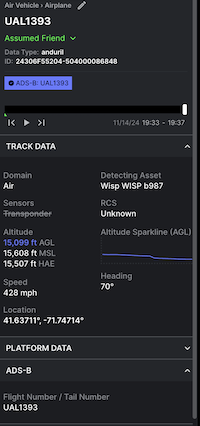
Representing time
The entity data model contains a few different timestamps. The most important timestamp
is the provenance.source_update_time field.
This field is required on every update and is the overall time of validity for the entity update.
Lattice will only apply an entity update if the new provenance.source_update_time is later than the previous one. Otherwise
it will drop the message.
Other components may include a timestamp when the latest time of observation for that particular
component is important to record for general situational awareness. For example, the
tracked_by contains
a last_measurement_timestamp that records the latest time the upstream source observed a target in a
camera frame, in a radar dwell, or an RF signal receipt.
In any update driven by a change in track data derived from sensor observation, the
tracked_by.last_measurement_timestamp will be the same as the provenance.source_update_time. However,
the tracked_by.last_measurement_timestamp may differ in a few different scenarios. For example:
- If a user overrides the track name, the
provenance.source_update_timewill reflect the time of that change but thetracked_by.last_measurement_timestampwill still reflect the time of observation. - If the integration extrapolates the target track forward in time (sometimes called a "coast"), it would
report a new
provenance.source_update_timewhile retaining the originaltracked_by.last_measurement_timestamp.